Unveiling the Power of Geothermal Resources
Ever wondered what’s behind those incredible geysers in Yellowstone, or why the hot springs all over the world feel so soothing? Well, the secret is right under our feet—geothermal resources. Yep, the heat from within the Earth isn’t just a legend; it’s a real-deal solution that’s meeting today’s energy needs. But what are geothermal resources exactly, and how do they work to give us such eco-friendly power? Let’s dig into this cool tech and get the lowdown.
How Do Geothermal Plants Work?
So, geothermal plants? They tap into Earth’s heat by reaching down to underground reservoirs full of hot water and steam. How’s it all happen? It starts with drilling wells into these reservoirs, bringing the hot goods up to the surface. Depending on how hot and pressurized the steam is, you get different types of geothermal plants like dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle—all turning that heat into electricity.
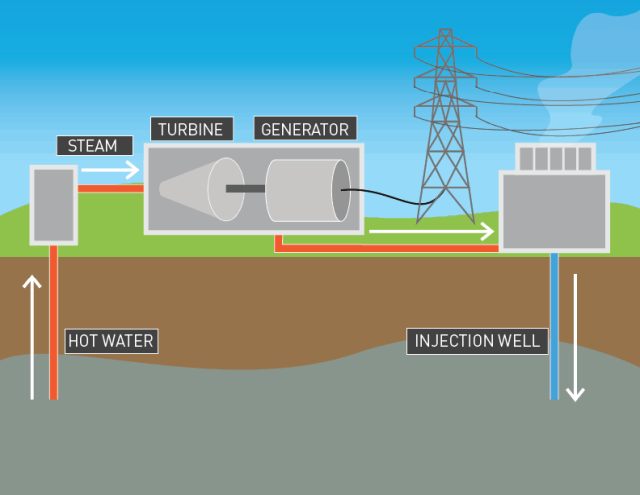
Take dry steam plants, for instance. They snatch steam right out of the ground and use it to spin turbine generators. Flash steam plants, on the other hand, yank up high-pressure hot water into cooler spots where it turns into steam in a flash—literally—that then powers generators. And binary cycle plants? They’re kind of neat. Hot water heats up a second liquid that boils at a lower temp, vaporizing it to churn the turbines.
The Benefits of Geothermal Energy
Now that we’ve got a handle on how these plants tick, why are they such a big deal in the sustainable energy game? First off, geothermal energy is super clean—it’s got almost zero emissions, which is huge for tackling climate change. Plus, it’s reliable; it doesn’t matter if it’s sunny or windy, this power source is always on. It also uses less land than other renewables and keeps going strong as long as it’s managed right, tapping into an endless heat supply from below.
Impact on Global Climate Change
Geothermal energy is a champ in slashing carbon footprints, especially compared to fossil fuels that cough up loads of CO2. By lowering emissions, geothermal helps keep global temperatures stable and cuts down on air pollution. Switching to this clean energy could mean a fresher, healthier planet for the next generations.

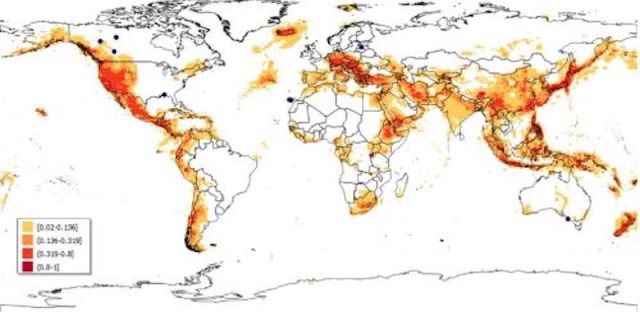
Global Leaders in Geothermal Energy
Want to know where geothermal is making big waves? Look at countries like Iceland and New Zealand, where volcanoes and hot spots make it easy to harness this power. Iceland alone gets over 25% of its electricity from geothermal! Other key players include the US (California’s big on this), Indonesia, and Kenya, each using their unique geologic features to boost their energy game.
Technological Advancements by 2025
Fast forward to now, 2025, and the leaps in geothermal tech have been game-changing. Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) are a big deal—they let us create hotspots where none existed naturally. Plus, smarter drilling tech means lower costs and better efficiency. Ever heard of tougher drill bits that can take the heat? That’s allowing us to dig deeper and tap into more of Earth’s natural warmth.
Economic Perspective: Cost Analysis vs Fossil Fuels
When stacking geothermal against fossil fuels, the initial price tag might make you pause—geothermal setups aren’t cheap upfront. But look long-term and the picture shifts. Lower running costs and minimal upkeep make geothermal more and more cost-effective, especially with a little help from government incentives.
Local and Global Benefits
Geothermal isn’t just about generating clean energy. Locally, it powers up jobs and economic activity without trampling over communities or the environment. Globally, it’s a key player in achieving sustainable development goals by providing stable, reliable energy—essential for lifting global living standards.

As we push forward to a greener future, embracing geothermal isn’t just smart for the environment—it’s a savvy economic move too. With ongoing innovations and strong policies to back it up, this powerful resource is ready to take center stage in our quest for sustainable energy solutions.
