Introduction to Metamorphosis in Insects
Ever caught yourself marveling at the wild process of metamorphosis? It’s this amazing biological phenomenon where insects switch up from their junior forms to completely new adult versions, each perfectly tweaked for their unique roles and settings. And sure, we all know the story of caterpillars morphing into butterflies, but that’s just the tip of the iceberg. Loads of insects go through this mind-boggling transformation, an absolute showcase of nature’s engineering smarts.
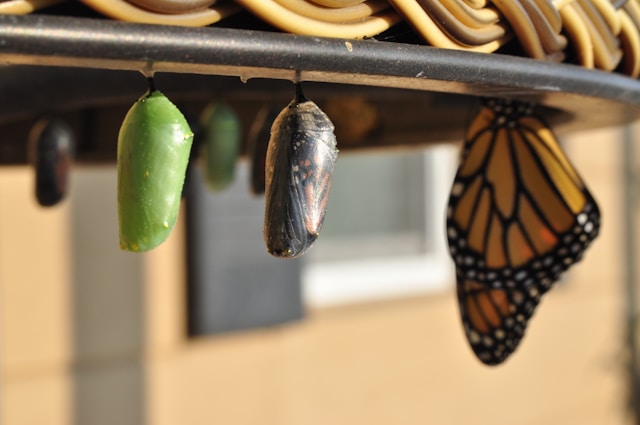

There are two main types of metamorphosis: complete and incomplete. In complete metamorphosis, we’re talking about four distinct life phases: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. On the flip side, incomplete metamorphosis skips the pupa stage and includes just three phases: egg, nymph, and adult, with the nymph typically looking like a mini version of the adult. Each method has its own slick strategies and advantages, helping these critters make it and thrive in what are often tough and competitive ecosystems.
The Science Behind Metamorphosis
To really get a grip on metamorphosis, we’ve got to dive deep into the science part of it. Hormones inside the insect are mega important in this process. For example, the juvenile hormone and ecdysone are in charge of the developmental dance through these stages. A dip in juvenile hormone levels kicks off pupation for those going the route of complete metamorphosis.

What happens inside the pupa is honestly miraculous. Cells are all over the place—some dying off, others morphing into the structures needed for adult life, like wings, antennae, and the bits needed for reproduction. This whole complex reorganization is managed by the insect’s genetic code, pulling off a series of developmental steps that culminate in the adult insect features.
And what’s super intriguing is how these processes vary wildly among species, each adapted to its own ecological niche and survival tricks. Like, take a butterfly’s colorful wings—those aren’t just for show! They’re crucial for managing body temperature and dodging predators.
Fascinating Examples of Insect Metamorphosis
Butterflies and Moths
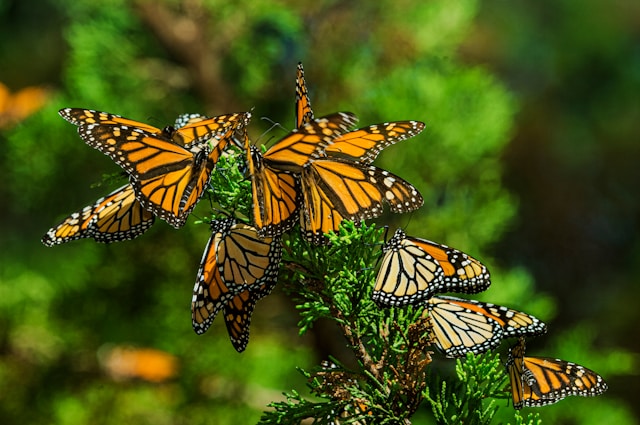

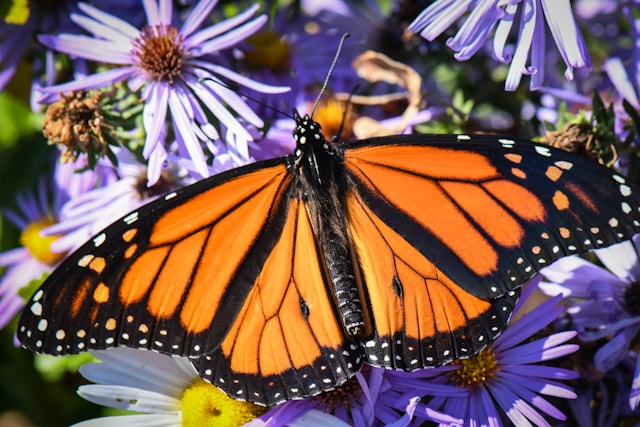
Let’s start with the usual suspects of metamorphosis: butterflies and moths. The trek of the monarch butterfly is particularly stunning. From a teeny egg on a milkweed leaf, it pops out as a munching caterpillar, only to cocoon itself into a chrysalis. Inside this safe space, it totally reworks its body to emerge as a vibrant butterfly, ready to migrate thousands of miles.
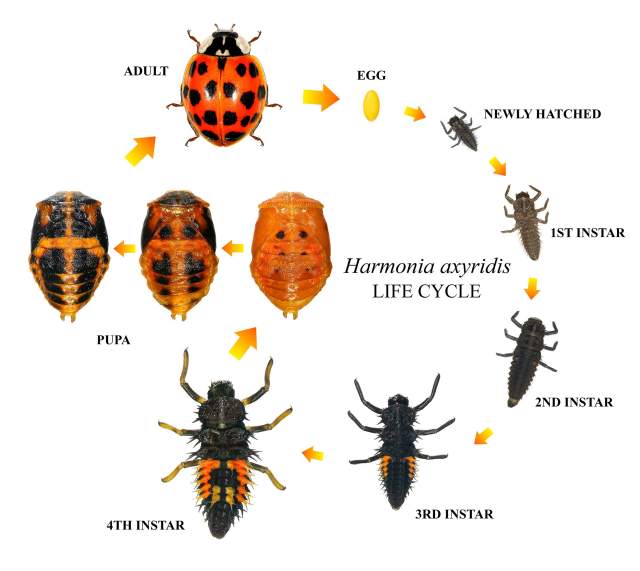
Beetles
Now, beetles have a transformation that’s just as dramatic. Take the ladybug (or ladybird), which starts off as a hungry larva chomping down aphids, then shifts into the well-known red-and-black spotted beetle. This change is not just a new look—it’s a whole new lifestyle.
Flies
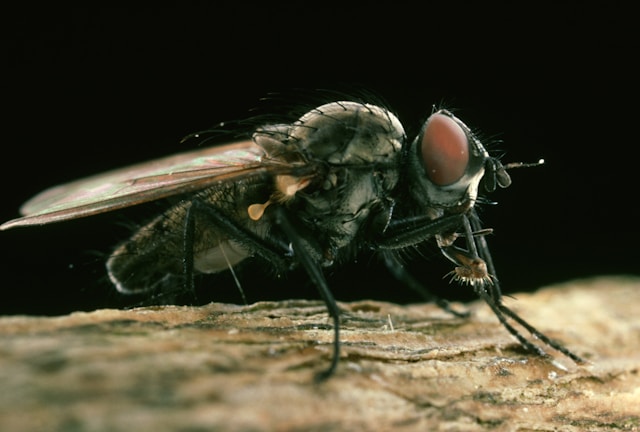

And don’t forget about the housefly—an ace at complete metamorphosis. They start as eggs in decomposing stuff, turn into totally legless and blind maggots, before hunkering down in a hard-case cocoon. And what emerges? Adult flies, ready to zoom around.
Each of these examples highlights how metamorphosis custom-fits these creatures to their roles in nature—be it pollinating plants or controlling pests—and underlines their importance in various ecosystems.
The Role of Metamorphosis in Ecosystems
Metamorphosis really shakes up ecosystems worldwide. By letting insects fill different ecological slots at different life stages, it cuts down on resource competition between the youngsters and adults. Like, caterpillars hog all the leaves, leaving the nectar for adult butterflies.
Plus, this transformation affects other species, too. Birds might snack on caterpillars but steer clear of adult butterflies, which might taste bitter or carry toxins from their larval diet. This interdependence is crucial for keeping ecosystems in balance.
Also, by splitting their lifecycle into distinct phases, insects can better manage population control and resource sharing—key for sticking around through environmental changes.
Conclusion: Reflecting on Nature’s Ingenious Designs
Thinking about these transformations deepens our appreciation for nature’s complexity and ingenuity. Metamorphosis isn’t just about survival; it’s a finely honed adaptation that showcases the evolutionary prowess to thrive in practically any niche.
As we zoom in on these astonishing transformations—from hungry larvae to complex adults capable of flight or camouflage—we see nature’s strategy for ensuring survival through perfectly engineered changes.
So next time you spot an insect, take a moment to think about its life story—a tale of transformation that might just shine a light on resilience and adaptation that’s relevant way beyond the natural world. Isn’t it incredible what we can learn from these tiny creatures among us?
